Dr. Nate here again with my lovely wife, Dr. Christine, and we want to talk to you today about dental cavities. I remember when I heard this crazy stat. Back in 2016, the CDC said that 90% of adults have had a cavity, but this is crazier, one in four adults in the US has untreated cavities. Okay, so let us talk about cavities.
What is A Cavity?
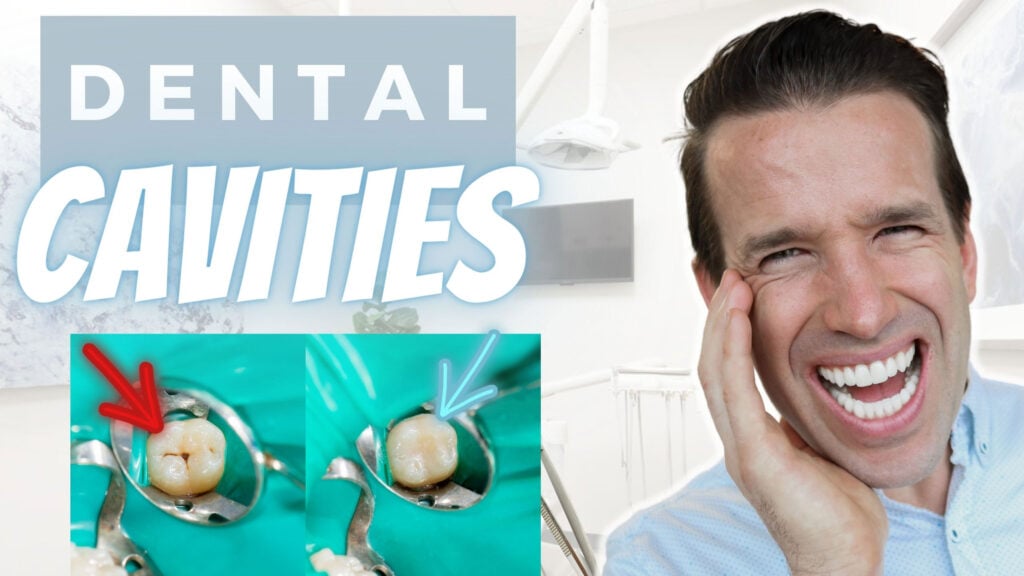
A cavity is an actual hole in the tooth that forms when you’re eating foods that are high in sugar or processed carbohydrates, which causes for the bacteria such as S. mutans bacteria to take in those food particles and metabolize them. The byproduct of that metabolism is an acidic substance. Over time that acid erodes away the dental enamel
You have bacteria that are covering your teeth, these bacteria will take in the sugar that we are eating in our diets, they’ll metabolize it, create acid, and if you do not brush or floss that acid off your teeth, the acid just gradually eats and eats, and eats away at the teeth. And you know what? It loves to form in those little cavities, those little pits, and fissures, the little areas.
Therefore, if the bacteria eats the outer surface of our teeth, it can then start eroding away the softer inner portion called dentin. Dentin is not nearly as strong as the enamel. So, you might have these little, little tiny dots on the enamel, on the outer surface of your teeth, but once that bacteria gets down into the dentin, it will spread like crazy. And if it gets close enough to the pulp chamber, what do we need to do? A root canal! If the bacteria continue to spread into the tooth and go deep enough, they will reach the nerves and pulp chamber. If the cavity and bacteria reach the inner portion of the tooth, you will likely need a root canal procedure. A root canal is essentially a really large cavity that has now entered the nerves and blood vessels of the tooth.
Why Do Cavities Hurt?
Yes, cavities hurt. Once it gets big enough, a cavity will hurt a lot because the nerves inside of the tooth are compromised now that that strong protective enamel on top is no longer covering and protecting the tooth. As bacteria start to infiltrate the tooth, they can work their way down into the pulp chamber, which is where all the nerve endings are and where the blood flow is through the tooth.
Once the bacteria gets into the inner portion of the tooth, then the tooth starts to get inflamed. And so, that inflammatory process causes great pain. It’s one of the worst pains you could have when you have a big toothache. That’s exactly what it is.
Okay, so now we know what a cavity is. We know why it causes so much pain. Now, how the heck do we treat these cavities?
Treating Cavities
So, when it’s a small, small little cavity and it’s in through the enamel layer, just barely into the dentin layer, what we do is we remove the decayed structure, remove the decay tooth structure, and we fill it with a filling. It’s pretty straightforward. You just take out all the decayed tooth structures and put a small filling on the tooth.
What if it has gotten a little bit bigger? Maybe the decay has taken out two-thirds of the tooth structure. You can’t just do a filling anymore. It is way too big. We do something that is called a dental crown.
What if it’s got even bigger? The decay’s gone through the enamel, that protective layer, through the dentin, the foamy layer, the not-as-strong layers as the enamel, and it’s even gone into the pulp chamber. And the pulp chamber is where the nerves and the blood vessels of the tooth are. If it gets into that area, you’re going to need a root canal.
Sometimes, if it’s gotten that big, we might also give you antibiotics to help with some of the infection. On top of that root canal, we will add a dental crown.
If the cavity has gotten even larger then you may not be able to fix it and it may need to be extracted. If you extract a tooth you should get it replaced with either a dental bridge or dental implant.
You always want to replace a missing tooth because if you leave a missing tooth, it leads to bone loss and disfiguration of the jaw and the facial structures, and your teeth start to shift, and that causes all kinds of other problems that you don’t want to start.
How Do Dentists Know You Have a Cavity?
Well, before you even go to the dentist, sometimes you can tell if you have a cavity if you notice some sensitivity to cold or sometimes hot. You may also notice when you’re eating something, maybe sweets, it can start to get sensitive. You may also not feel anything at all. That’s why it’s very important to come to your dentist every six months for your checkups.
We take x-rays, we do an exam, and we check, and we can see, we detect cavities that frequently, most people can’t see. Sometimes though, if you open up your own mouth and you take a close look at your teeth, you can see some dark spots on your teeth. You can see cavities that maybe have started to form.
How Do You Prevent Dental Cavities?
I love to talk about this because that’s near dear to my heart, but if you have crowded teeth or malaligned teeth, then come on in because we need to straighten those up because if you’re brushing and flossing and the teeth are overlapping, you probably can’t brush and floss them well, and they’re going to be way more prone to decay.
Along with that, you have to ensure you’re proper brushing and flossing. I don’t think I know a single dentist with a manual toothbrush. Almost everybody I know, actually everybody I know, uses an automatic toothbrush just because they’re a thousand times better than a manual toothbrush. Make sure you’re brushing and flossing correctly.
You don’t have to floss all your teeth, just the ones you want to keep. That’s what I always tell all my patients. So, make sure you also come in for your routine cleanings every six months so that we can detect anything going on before it turns into this whole big thing. Fix it while it’s small.
Also make sure that your diet is not full of processed foods, like highly-refined carbohydrates, and sugary foods. That’s precisely what cavity-causing bacteria love to feast on and wreak havoc in your mouth.